What Is The Pavlov Theory: Unraveling The Science Of Conditioned Responses
Pavlov’S Classical Conditioning
Keywords searched by users: What is the Pavlov theory pavlov theory of learning, pavlov theory pdf, ivan pavlov theory summary, pavlov theory year, application of pavlov theory in education, pavlov experiment, pavlov dog theory on humans, pavlov theory of personality
What Is Pavlov Theory Of Classical Conditioning?
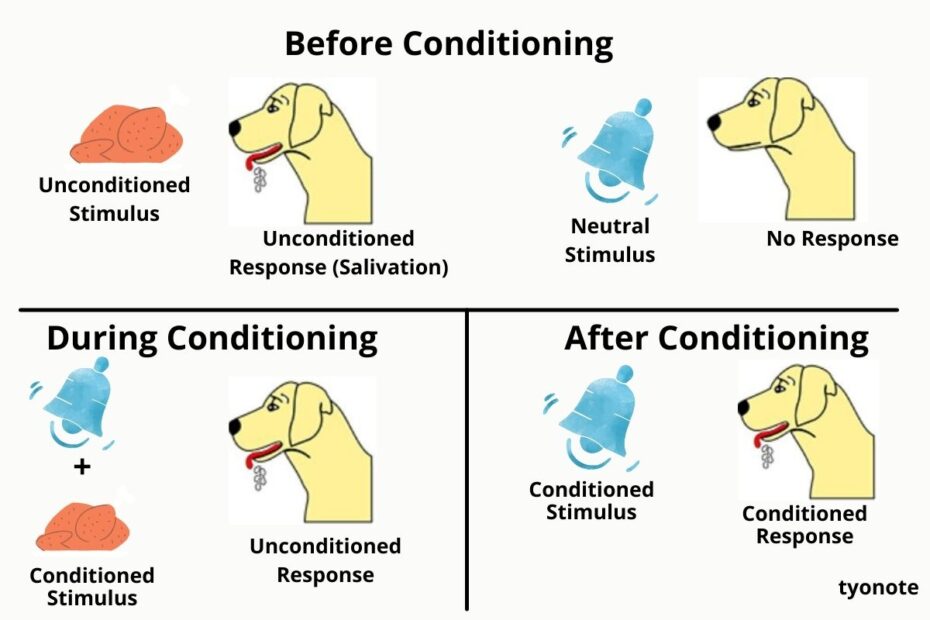
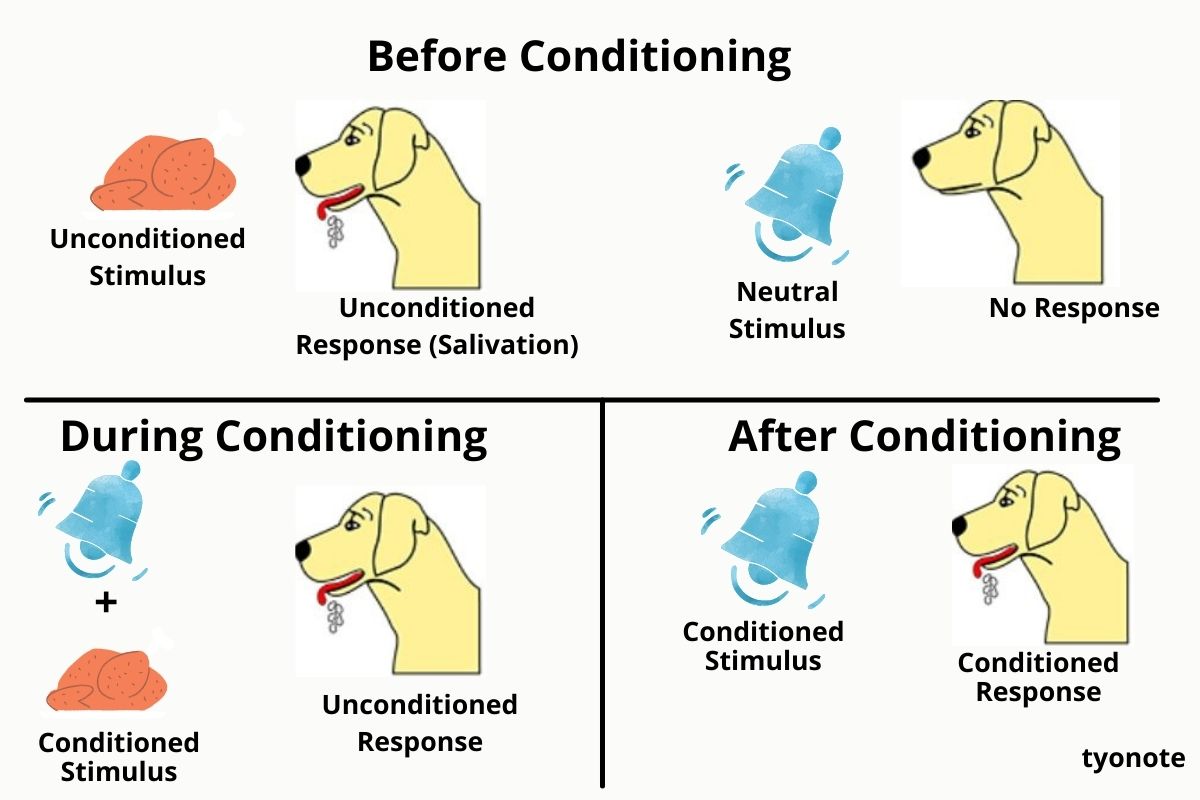
Classical conditioning theory, often associated with Ivan Pavlov’s groundbreaking research, is a fundamental concept in psychology that explains how behaviors are acquired through the association of a neutral stimulus with a positive one. In the classic example of Pavlov’s dogs, the neutral stimulus was the sound of a bell, while the positive stimulus was the expectation of food. When these two stimuli were consistently paired together, the dogs eventually learned to associate the bell with food and began to salivate even when food was not present. This learned behavior, where the dogs’ salivation response was triggered by the bell, is termed a conditioned response. Classical conditioning theory helps us understand how various behaviors can be acquired through the process of associative learning, where previously neutral stimuli become powerful triggers for specific responses. This theory has far-reaching implications in psychology, influencing our understanding of how humans and animals learn and adapt to their environments.
Which Learning Theory Is Pavlov Known For?
Pavlov is renowned for his groundbreaking Theory of Classical Conditioning. This theory stems from his meticulous observations involving dogs and their salivary responses. According to Pavlov, the dogs had acquired a learned response whereby they would salivate upon seeing the white lab coats worn by the research assistants. This response was a result of the dogs associating the lab coats with the presentation of food. This concept of classical conditioning, developed by Ivan Pavlov, has had a profound impact on our understanding of how organisms learn and adapt to their environments.
How Did Pavlov Define Psychology?
Ivan Pavlov’s definition of psychology is closely associated with the theory of behaviorism, which is alternatively known as behavioral psychology. Behaviorism posits that every human behavior can be acquired and understood through a fundamental process known as conditioning. This theory underscores the idea that all human actions can essentially be considered as responses triggered by various stimuli within their surrounding environment. In essence, Pavlov’s perspective on psychology emphasized the significance of studying how external influences and experiences shape human behavior.
Details 17 What is the Pavlov theory

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2794859-article-classical-conditioning-5ac50cc9c5542e0037d54692.png)


Categories: Summary 79 What Is The Pavlov Theory
See more here: future-user.com

Pavlov’s theory suggests that emotional responses can also be conditioned. This means that our emotional reactions to certain stimuli can be shaped and influenced by our past experiences and associations.What Is Classical Conditioning Theory? Classical conditioning theory states that behaviors are learned by connecting a neutral stimulus with a positive one, such as Pavlov’s dogs hearing a bell (neutral) and expecting food (positive). The learned behavior is called a conditioned response.Pavlov’s Theory of Classical Conditioning
Based on his observations, Pavlov suggested that the salivation was a learned response. Pavlov’s dog subjects were responding to the sight of the research assistants’ white lab coats, which the animals had come to associate with the presentation of food.
Learn more about the topic What is the Pavlov theory.
- Ivan Pavlov’s Theory – Structural Learning
- What Is Classical Conditioning? – WebMD
- Pavlov’s Dogs and the Discovery of Classical Conditioning
- Ivan Pavlov Contribution to Psychology | Law & Theory
- Pavlov’s Theory of Behaviorism: Key Concepts – PHILO-notes
- Classical Conditioning: Examples and How It Works – Verywell Mind
See more: future-user.com/your-money