기벡
기벡(GiBic: GIL LAB Brain Inspired Computing)은 오픈소스 딥러닝 라이브러리 중 하나로서, 대한민국 대학교인 성균관대학교와 한국과학기술연구원(KIST)이 공동 개발하였다. 기벡은 뇌와 유전자 등 구조적, 기능적으로 영감을 받아 딥러닝 알고리즘을 개발하였다. 이러한 딥러닝 알고리즘은 인공지능 분야에서 가장 선도적인 기술 중 하나로 꼽히며, 이미 포털 사이트와 IT 기업 등에서도 활용되고 있다.
기벡의 장점
기벡은 다음과 같은 장점을 가지고 있다.
1. 높은 처리 속도: 기벡은 고성능 병렬 연산 프레임워크인 커다란 데이터 처리 라이브러리(CUDA)를 지원하기 때문에 대규모 데이터 처리에 매우 효과적이다.
2. 실시간 분석: 기벡은 대규모 비디오 데이터를 빠르게 처리할 수 있어 기계 학습, 컴퓨터 비전, 자연어 처리 등 분야에서 유용하게 이용된다.
3. 보안성: 기벡은 높은 보안성을 제공하여 보안 규정을 준수하는 기업에서는 강력한 보안성을 보장할 수 있다.
기벡이 지원하는 언어
기벡은 파이썬과 C++ 언어를 모두 지원한다. 이는 기업 또는 개인이 알고리즘 및 데이터 처리를 위해서 선호하는 언어와 호환 가능하다는 것을 의미한다. 또한, 기벡은 파이썬의 인기함에 따라 파이썬 인터페이스를 강화시키기 위해 지속적으로 업데이트 하고 있다.
기벡을 사용한 주요 프로젝트
기벡은 다양한 분야에서 활용되고 있으며, 특히 대규모 데이터 처리가 필요한 분야에서 많이 사용된다. 기벡을 사용한 주요 프로젝트는 다음과 같다.
1. 빅데이터 분석: 기벡은 대우조선해양, 삼성전자, 현대자동차, 라인 등에서 빅데이터 분석에 사용되었다. 이를 통해 데이터 기반 의사 결정과 효율적인 비즈니스 전략 수립에 도움을 주고 있다.
2. 음성인식: 기벡은 샤오미 등 내비게이션, 인공지능 스피커 등에서 음성인식에 활용되고 있다.
3. 자율주행: 기벡은 테슬라와 구글 등에서 자율주행을 위한 기술 연구에 활용되고 있다.
기벡 기반의 상용 서비스
기벡을 사용한 상용 서비스는 다양한 분야에 걸쳐서 이루어지고 있다. 이들 서비스의 몇 가지 예시를 소개하면 다음과 같다.
1. LG CNS의 ‘가상 대리석(AR용 키 해킹)’ – 기벡을 이용한 AR 기술을 이용하여 캐릭터의 움직임과 대화 등과 같이 인간의 동작과 음성을 캐시캐쉬에 학습시켜 가상 캐릭터가 생생하게 움직이고 대화를 나누는 서비스이다.
2. KT의 ‘휘슬리(스마트홈 AI 스피커)’ – 기벡을 이용한 음성인식 시스템을 탑재하여 스마트홈을 보다 편리하게 제어할 수 있는 서비스이다.
3. SK텔레콤의 ‘T맵 지도 앱’ – 기벡을 활용하여, 출발과 도착지 입력 없이 출발 지점의 지명과 방향만 입력해도 자동으로 목적지까지 안내해주는 서비스이다.
기벡의 미래 전망
기벡은 현재 기업, 연구 기관 등에서 널리 사용되고 있으며, 더욱 더 활성화될 것으로 예상된다. 더 나아가, 기벡은 AI 기술 발전의 중심이 될 것으로 기대되고 있다.
특히, 기벡은 인공 신경망 방식의 보다 더 세밀한 모델링을 위한 최신 알고리즘을 제공하며, 이러한 모델링은 딥러닝 분야에서 지속적으로 연구되고 있다. 이러한 연구는 새로운 분야에서 어플리케이션 개발을 다시금 도약시키는 기반 연구일 수 있다.
FAQs
1. 기벡은 어떠한 분야에서 사용될 수 있나요?
– 기벡은 빅데이터 분석, 음성인식, 자율주행 등 여러 분야에서 사용될 수 있습니다.
2. 기벡이 지원하는 언어는 어떤 것이 있나요?
– 기벡은 파이썬과 C++ 언어를 모두 지원합니다.
3. 기벡 기반의 상용 서비스를 알려주세요.
– LG CNS의 ‘가상 대리석(AR용 키 해킹)’, KT의 ‘휘슬리(스마트홈 AI 스피커)’, SK텔레콤의 ‘T맵 지도 앱’ 등이 기벡 기반의 상용 서비스입니다.
4. 기벡의 미래 전망은 어떠한가요?
– 기벡은 AI 기술 발전의 중심이 될 것으로 예상되며, 딥러닝 분야에서 지속적인 연구가 진행될 것으로 예상됩니다.
5. 기벡을 사용한 곳은 어디인가요?
– 대우조선해양, 삼성전자, 현대자동차, 라인, 테슬라, 구글 등에서 기벡을 사용하고 있습니다.
사용자가 검색한 키워드: 기벡 기하 목차, 기하 단원명, 기하 교과서, 수능 기하, 공간벡터 킬러, 기하 교육과정, 기하 선택
Categories: Top 72 기벡
[메가스터디] 수학 현우진 쌤 – REMARK 사관학교 기출 기하와벡터(가형)
여기에서 자세히 보기: future-user.com
기하 목차
Korean language is known for its unique writing system known as “Hangul.” One of the essential aspects of Korean language learning is grammar, which includes “기하 목차” (giha mokcha). It refers to the hierarchical ordering of clauses, phrases, and words in Korean sentences. In this article, we will delve into the details of 기하 목차 and how it works in the Korean language. We’ll also provide some frequently asked questions about this aspect of the Korean language to help you better understand its importance.
What is 기하 목차?
기하 (giha) refers to the hierarchical order of elements in a sentence, while 목차 (mokcha) means table of contents or an ordered list. In other words, 기하 목차 explains how the different elements of a sentence are ordered and arranged according to their level of importance in conveying a message effectively.
The hierarchical ordering of elements in Korean sentences is based on the principle of subject-verb-object (SVO) word order. However, Korean sentences do not always follow a strict SVO pattern. The order in which the elements are placed often depends on contextual factors that determine the focus of the sentence.
For example, in the sentence “나는 사과를 먹었다” (na-neun sa-gwa-reul meog-eot-da), “나는” (na-neun) means “I,” “사과를” (sa-gwa-reul) means “apple,” and “먹었다” (meog-eot-da) means “ate.” In this sentence, the SVO word order is followed, with “I” as the subject, “apple” as the object, and “ate” as the verb. However, the sentence puts more emphasis on the action of eating than on the apple itself.
How does it work?
기하 목차 in Korean sentences follows a hierarchical ordering that emphasizes the most essential elements of a sentence. Additionally, it determines the level of importance of each element in conveying meaning and context. In Korean, the subject is usually stated first, followed by the object and then the verb.
If there is a modifier or adverb, it is usually placed in front of the word it modifies, which affects the focus of the sentence. For example, the sentence “우리는 저녁에 식사를 했다” (u-ri-neun jeo-nyeok-e sik-sa-reul haet-da) literally means “We in the evening meal had.” In this sentence, the subject “우리” (u-ri) is emphasized, and the modifier “저녁에” (jeo-nyeok-e) places emphasis on the time of day when the meal was eaten. The sentence places less emphasis on the verb, “했다” (haet-da), making it more passive in tone than active.
In some cases, the object can be placed before the subject or verb, depending on the sentence’s context. For example, the sentence “사과를 나눴어요” (sa-gwa-reul na-nwa-sseo-yo) means “I divided (or shared) the apple.” In this sentence, the verb “나눴어요” (na-nwa-sseo-yo) comes after the object “사과를” (sa-gwa-reul). This order places emphasis on the apple, indicating that it is the most important element of the sentence.
Examples of 기하 목차
Let’s take a look at some examples that illustrate the principles of 기하 목차 in Korean sentences:
– “배가 고프다” (bae-ga go-hup-da) means “I’m hungry.” In this sentence, the subject “배” (bae) comes first, followed by the adjective “고프다” (go-hup-da), which indicates hunger.
– “일어나니까 머리를 감았어요” (i-reo-na-ni-kka meo-ri-reul gam-as-seo-yo) means “I tied my hair up after waking up.” In this sentence, the adverbial clause “일어나니까” (i-reo-na-ni-kka) comes first, indicating when the action occurred. The subject “머리를” (meo-ri-reul) comes next and is followed by the verb “감았어요” (gam-as-seo-yo).
– “저기 그분이 오시면 알려주세요” (jeo-gi geu-bun-i o-si-myeon al-lyeo-ju-se-yo) means “Please let me know when that person over there comes.” In this sentence, the pronoun “저기” (jeo-gi) comes first, indicating the location of the person. The subject “그분이” (geu-bun-i) follows, followed by the verb “오시면” (o-si-myeon), indicating the conditional clause “if he/she comes.” The sentence ends with the imperative verb “알려주세요” (al-lyeo-ju-se-yo), meaning “please let me know.”
FAQs on 기하 목차
1. Is it essential to understand 기하 목차 to learn Korean?
Yes, it is crucial to understand 기하 목차 in Korean because it reflects the hierarchical ordering of elements in a sentence, which plays a vital role in conveying meaning and context. Understanding 기하 목차 helps learners to identify the nucleus of the sentence and how the different elements interact to produce meaning.
2. How does 기하 목차 differ from other languages’ sentence structure?
기하 목차 is unique to Korean language. While other languages such as English follow a subject-verb-object (SVO) word order, Korean sentences may have a variety of word arrangements, depending on the contextual factors involved. Additionally, 조사 (josa) or particles are added to the end of words to indicate their function in the sentence. This aspect of Korean language requires dedicated attention from learners to understand.
3. What are some mistakes to avoid when using 기하 목차 in Korean sentences?
One common mistake learners make when using 기하 목차 in Korean sentences is using the English sentence structure in place of the Korean structure. It is essential to pay attention to how words are arranged in a sentence, as it reflects the writer or speaker’s intentions to convey meaning. Another common mistake is failing to use particles (조사) correctly, which can confuse the reader or listener about the intended focus of the sentence.
Conclusion
In summary, 기하 목차 is a crucial aspect of the Korean language that reflects the hierarchical order of elements in a sentence. Understanding 기하 목차 is essential to learning Korean because it reflects the language’s unique structure and helps learners understand how sentences work in a meaningful context. By following the guidelines of 기하 목차 and paying close attention to the roles and functions of each sentence element, learners can enhance their Korean language proficiency and communicate more effectively.
기하 단원명
The Korean education system places a significant emphasis on mathematics, and geometry is no exception. In this article, we will delve into the details of what 기하 단원명 is, and why it is important to the Korean education system.
What is 기하 단원명?
기하 단원명 is a term that refers to the geometry section of the Korean mathematics curriculum. Geometry is taught in Korean schools from the third grade upwards. The subject covers a range of topics that are designed to help students learn about the properties of shapes and sizes. Topics covered in 기하 단원명 include line, angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, and three-dimensional shapes like cubes, cones, and cylinders.
The Korean mathematics curriculum is designed to be progressive, and so the topics in 기하 단원명 get progressively complicated as students move up the grade levels. For example, in the third grade, students learn about basic shapes, while fourth-graders learn about angles, lines, and the properties of two-dimensional shapes. By the time students reach the sixth grade, they are studying three-dimensional shapes, angles, and triangles.
Why is 기하 단원명 important?
Geometry plays an important role in mathematics, and the study of geometry is essential for problem-solving, logical thinking, analytical reasoning, and developing spatial awareness. Basic geometry concepts like lines and angles are also essential to other subjects like physics and engineering.
The study of geometry can provide students with a range of skills that can be used throughout their lives. These skills include the ability to:
– Analyze shapes and identify their properties.
– Use mathematical formulas to determine the dimensions and sizes of objects.
– Connect geometry concepts to other subjects, like physics and engineering.
– Solve complex problems using logical reasoning and analytical thinking.
By including geometry in the mathematics curriculum, Korean educators are preparing students for their future academic and professional lives. Students who have a strong foundation in geometry are more likely to excel in fields like engineering, architecture, and science.
FAQs about 기하 단원명
1. What are some of the topics covered in 기하 단원명?
기하 단원명 covers a range of topics that include lines, angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, and three-dimensional shapes like cubes, cones, and cylinders.
2. When is geometry introduced to Korean students?
Geometry is introduced to Korean students in the third grade.
3. Why is geometry important in mathematics?
Geometry is important in mathematics because it helps students develop problem-solving skills, logical thinking, analytical reasoning, and spatial awareness. Geometry concepts are also essential in other subjects like physics and engineering.
4. Can students connect geometry to other subjects?
Yes, students can connect geometry to other subjects like physics and engineering. Understanding geometry can help students develop a deeper understanding of these subjects.
5. What skills can students gain from studying geometry?
Students can gain a range of skills from studying geometry, including the ability to analyze shapes and identify their properties, use mathematical formulas to determine the dimensions and sizes of objects, connect geometry concepts to other subjects, like physics and engineering, and solve complex problems using logical reasoning and analytical thinking.
Conclusion
기하 단원명 is a crucial part of the Korean mathematics curriculum. The study of geometry provides students with a range of skills that are essential for problem-solving, logical thinking, analytical reasoning, and developing spatial awareness. Basic geometry concepts are also essential in other subjects like physics and engineering. By including geometry in the mathematics curriculum, Korean educators are preparing students for their future academic and professional lives.
주제와 관련된 이미지 기벡
![[메가스터디] 수학 현우진 쌤 - REMARK 사관학교 기출 기하와벡터(가형) [메가스터디] 수학 현우진 쌤 - REMARK 사관학교 기출 기하와벡터(가형)](https://rausachgiasi.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/hqdefault-649.jpg)
기벡 주제와 관련된 이미지 9개를 찾았습니다.


![기벡-(5)공간도형,공간좌표-30번 [200709 가24] - YouTube 기벡-(5)공간도형,공간좌표-30번 [200709 가24] - Youtube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/0zqSr5SLGBs/maxresdefault.jpg)



 학원 소식 | 엄마만 알고있는 비밀” style=”width:100%” title=”대치동의 비밀수학, 강의하는 과외식 수업” 기벡기본/확통실력 마스터 주말 신설반 모집 > 학원 소식 | 엄마만 알고있는 비밀”>
학원 소식 | 엄마만 알고있는 비밀” style=”width:100%” title=”대치동의 비밀수학, 강의하는 과외식 수업” 기벡기본/확통실력 마스터 주말 신설반 모집 > 학원 소식 | 엄마만 알고있는 비밀”>

![카드뉴스] 고교 이과생, '기하와 벡터' 배우지 않아도 될까요 | 연합뉴스 카드뉴스] 고교 이과생, '기하와 벡터' 배우지 않아도 될까요 | 연합뉴스](https://img.yna.co.kr/etc/inner/KR/2018/02/26/AKR20180226066500797_26_i_P4.jpg)








![기벡] 9. 공간도형(1) - YouTube 기벡] 9. 공간도형(1) - Youtube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/VUu0mMeWyO4/maxresdefault.jpg)


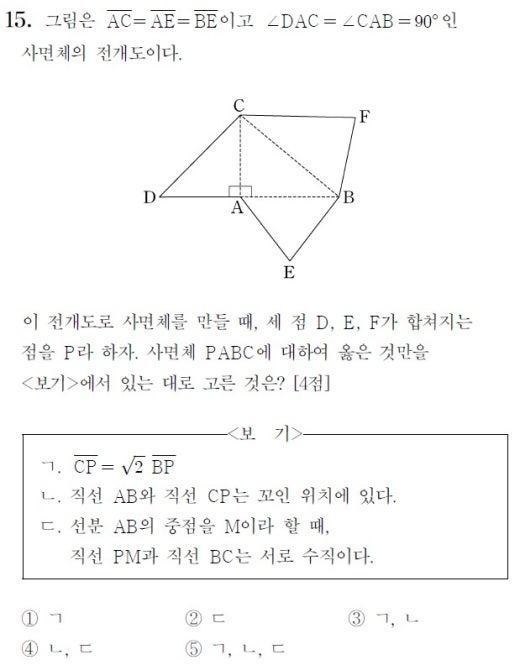







![수능난제 시즌1]2013 EBS 수능완성 기벡 7.공간도형 8번 - YouTube 수능난제 시즌1]2013 Ebs 수능완성 기벡 7.공간도형 8번 - Youtube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ilNWYgqmQUA/maxresdefault.jpg)





Article link: 기벡.
주제에 대해 자세히 알아보기 기벡.
- [개정전]기하와 벡터 개념총정리, 공식 총정리 : 네이버 블로그
- 기하와벡터 난이도가 어느정도입니까? – 오르비
- [카드뉴스] 고교 이과생, ‘기하와 벡터’ 배우지 않아도 될까요
- 기벡 개념정리 – 기하 개념 정리 – Studocu – Studocu
- 28132번: 기벡을 안배운다고?
더보기: future-user.com/wki